Effects on human comfort
The human body takes into chemical energy, as food and drink, and oxygen, and uses them to provide the energy metabolism. Some mechanical work can be done, but the most part is released as heat in the amount of 90 watts rest and 440 watts when doing heavy work.
A little radiation loss, if the surrounding surface cold and some as sensible heat by convection from the skin. The balance is taken as the latent heat, moisture from the tissues of the respiratory and sweat from the skin (see Table. 20.2). Shining losses will be very small if the person is dressed, and is ignored in this table.
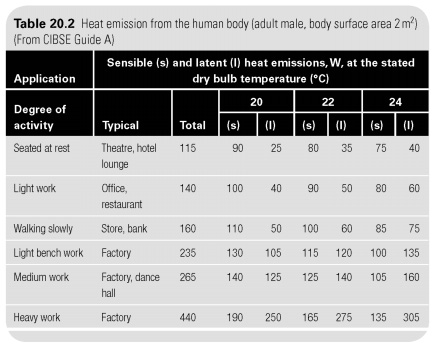
Prevents heat loss will depend on the area of skin exposed, air velocity and temperature difference between the skin and the environment. As D.B. approaches body temperature (36.9C) possible convective losses will be reduced to zero. At the same time, the loss of latent heat must increase to keep the body cool. It also should decrease to zero when wet bulb temperature reaches 36.9C.
In practice, the human body can exist in the dry bulb temperature is higher than the temperature of the blood, providing moisture is low enough to allow evaporation. The limiting factor is, therefore, one of the wet-bulb thermometer, not a dry bulb thermometer, and the closer to the top limits, the less heat to be rejected, and therefore less work can be done...
|

