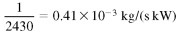Cooling towers
In a cooling tower, cooling the main mass of water that is obtained by evaporation of a small part of the air flow. Chilled water outlet of the tower will be 3-8 K warmer than the incoming air wet bulb temperature. (See also Chapters 21 and 22.) Amount of water evaporated takes its latent heat equal capacitor debt of about 2430 kJ/kg of evaporated, and will be approximately
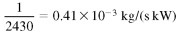
For capacitor load of 400 kW, evaporation least at the rate of 0.16 kg/sec.
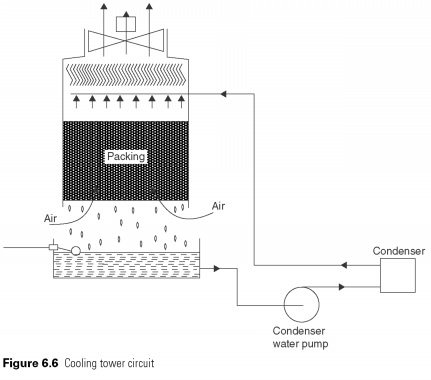
Chilled water drain tank pump and passed through the condenser. Warm water, then passes sprays or distribution of deflections on top of the tower, and falling in the air currents over the packages, which are very surface-to-air. Evaporation occurs couple of latent heat from the water body, which in connection with cooling (see Fig. 6.6).
Power consumption tower can be reduced using a fan or fan speed control under light load conditions. The exhaust tower, which in the outlet of the fan air flow may reach 10-15% of the fan performance of downtime. This is not the case, towers, where the fan is located in the supply air flow.....
|