Capacitor
Condenser heat exchanger that transfers heat from the refrigerant flowing within its tube fluid that flows through it. The result is that the heat content of the fluid flowing more it grows, while the refrigerant is condensed. This process enables the reuse of refrigerant for cooling of air or liquid in the evaporator. Capacitor removes heat from the cooling system.

Types of capacitors:
Capacitors can use either air or water for removal of heat from the refrigerant. Capacitors that release heat of air called air-cooled condensers, and those who reject heat to the water, called water-cooled condensers. For jobs below 100 tons of cooling capacity, air-cooled condensers are used in most cases. The more tonnage of the work, the greater the likelihood that water-cooled condensers will be used. System of more than 100 tons, cooling capacity, which use coolers for cooling water often use water-cooled condensers.
The vast majority of residential and light commercial equipment uses air-cooled condensers.

Air-cooled condenser shows the battery tube type commonly used in air conditioning and commercial refrigeration. Notice how similar it snorkels, fins, and General construction, for those on the D-X (evaporator) coil, shown previously. Condenser coils are manufactured in various shapes and sizes. Style fins may differ from the hard, lamella, as shown below, to sharp fins that have a ribbon-like appearance. Some fins were removed in this scheme, for easy viewing three pipes inside the coil.

Outside air (about 95F) is drawn over the condenser coil via a capacitor, fan, heat from the refrigerant flows from the hot refrigerant in the air. Even if the outdoor air is very high temperature, high pressure generated by the compressor refrigerant makes quite a bit warmer (120F saturation temperature or 170F the actual temperature with overheating)than air, so that the heat is transferred from the refrigerant in the air.
Refrigerant heat exchanger condenser hot gas line coming from the compressor discharge. Depending on the size of the coil, there may be a connection or multiple connections from the hot gas header, as shown here. Refrigerant way through the coil is shown here only one path, although there are many schemes, as is the hot gas to connect to a coil.

Temperature and state of the refrigerant as it passes through the condenser can be built on the basis of temperature and enthalpy (T-H) chart. Thick line shows the real state of R-22 refrigerant in the condenser pressure 263 pounds per square inch. In the process of condensation, heat content decreases approximately 125 BTU/lb to 42 Btu/lb; this creates the enthalpy difference approximately 83 Btu/lb. This loss of heat from the refrigerant is about 22% higher than the enthalpy, accumulated in the evaporator. The reason for the difference is that heat is added refrigerant after she leaves the evaporator. Compressor adds warmth when compressed gas from the evaporator. The capacitor must remove the heat added a compressor, as well as that gained in the evaporator, for the recovery of refrigerant in the proper condition to regain the evaporator, both the liquid and the gaseous mixture.
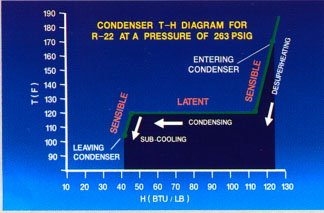
Refrigerant passes sensible, latent and, finally, a sensible heat transfer process as it flows through the condenser. In other words, the capacitor desuperheats, condenses, and subcools refrigerant. For more hypothermia is added in the condenser, in this case it is 15F.
The refrigerant enters the condenser, compressor outlet. At the outlet of the condenser, it flows metering device. Enthalpy of the refrigerant leaving the condenser same as the inlet of the evaporator (42 Btu/lb). We'll discuss this topic later...
|





