Thermoelectric Cooling
This system is used to move heat from one area to another using electric energy. Electrical energy instead of refrigerant, serves as a " carrier". A significant application of thermoelectric systems in portable coolers, water coolers, cooling scientific apparatus used in space exploration, and in the plane. The main advantage of this system is that there are no moving parts. Thus, the system is compact, quiet, and needs little service. Thermoelectric coolers, semiconductor equipment, used in applications where the temperature is stabilized, temperature, Cycling, or cooling below ambient temperature, are mandatory. There are many products with the use of thermoelectric coolers, including the CCD (charge coupled device) camera, laser diodes, microprocessors, blood analyzers and portable picnic coolers. Thermoelectricity based on the Peltier Effect, discovered in 1834, through which a direct current applied through two dissimilar materials causing a temperature drop. Peltier effect is one of the three thermoelectric effects, the other two, known as the Seebeck effect and the Thomson effect.
Whereas the last two effects are on a single conductor, Peltier effect is typical junction of the phenomenon. Three effects are connected to each other by a simple relationship (Godfrey, 1996).
Typical of thermoelectric module using two thin ceramic plates P-series and N-doped bismuth-telluride semiconductor materials sandwiched between them. Ceramic material on both sides of the thermoelectric adds rigidity and the necessary electrical insulation. N type of material excess of electrons, while the P type of material has a deficit of electrons. One P and N is a pair, as shown in Fig. 3.69. Thermoelectric couples (electrically in series and thermally in parallel. Thermoelectric module can contain from one to several hundred pairs. As the electrons move from the P type N-type material material through an electric socket, electrons jump to a higher energy state, absorbing heat energy (cold side). Continuing through the lattice of the material, electrons flow from the N-type material P-type material through an electric socket, dropping to a lower energy state and releasing energy in the form of heat to the heat sink (hot side). Thermoelectricity can be heated and cooled, depending on the current direction. In applications that require heating and cooling, the design should focus on cooling mode. Using thermoelectric heating mode is very efficient, as all internal heating (Joulian heat) and download from the cold side with the help of the pump hot side. This reduces the power required to reach the desired heating. 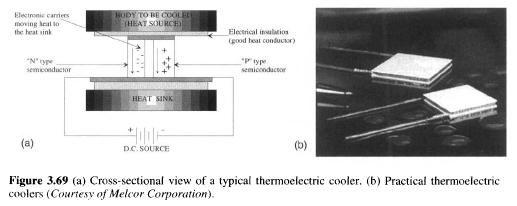
..
|
