Practical considerations and the COP
For a simple scheme, using as a working liquid Refrigerant R134a due to the evaporation of -5C and condensing at 35C, pressure and enthalpy will look as shown in Fig. 2.3:
- Enthalpy of liquid at the inlet of the evaporator = 249.7kJ/kg
- Enthalpy of saturated steam at the inlet of the evaporator = 395.6kJ/kg
- The cooling effect = 395.6 - 249.7 = 145.9kJ/kg
- Enthalpy of superheated steam outlet compressor (isentropic compression) = 422.5
After the vapour compression cycle uses energy to move energy, the ratio of these two quantities can be directly used as a measure of system performance. As noted in Chapter 1, this ratio is called the coefficient of performance (COP). The ideal or the theoretical cycle of compression vapor COP less Carnot COP due to deviation from ideal processes mentioned in Section 2.2. Ideal vapour compression cycle COP depends on the properties of the refrigerant, and in this regard some refrigerants are better than others.
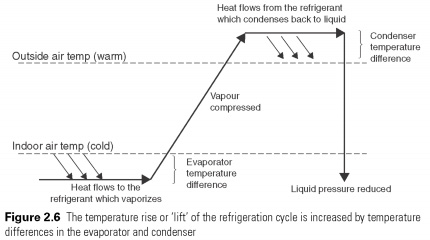
Heat transfer through the walls of the evaporator and condenser requires a temperature difference, as shown in Fig.
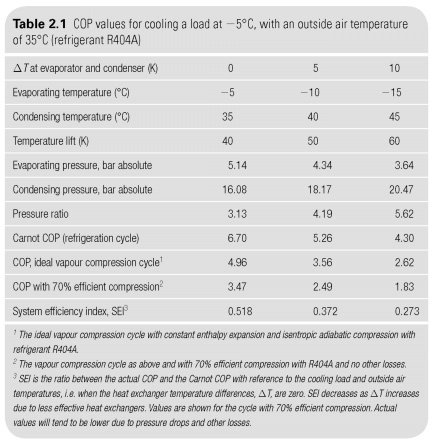
2.6. More heat exchangers, the lower the temperature differences, and so the closer the temperature of the liquid will download and secondary seal. The COP cycle depends on capacitor and a difference of temperatures of the evaporator (see Table. 2.1).
Table 2.1 shows how Carnot COP decreases as the cycle the temperature rises due to the higher heat exchanger large temperature differences.
The practical implications of the size of the heat exchanger can be summarized as follows:
More evaporator: (1) increase the suction pressure to give denser gas at the compressor inlet and therefore the greater the mass of gas for the volume, and therefore cooling; (2) increase the suction pressure, so a lower compression ratio and less energy to this obligation.
More capacitor: (1) low temperature condensation and cold water inside the expansion valve, allowing greater cooling effect; (2) reduction of discharge pressure, consequently, a lower compression ratio and less energy.
In the refrigeration contour of cooling of the room 0C using outside air at 30C to reject heat. R134a Refrigerant. The difference of temperatures of the evaporator and condenser 5 K. Find Carnot COP for the process, Carnot COP for cooling cycle and the ideal vapour compression cycle of the COP, when using R134a.....
|


