Thermostats
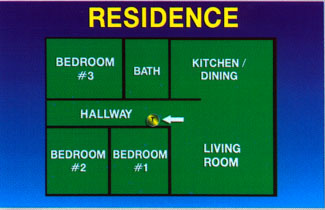
Thermostat enables or disables the cooling or heating at a given temperature. To do this, the unit should have a temperature sensor. As a rule, the thermostat on the wall in the room or in the hallway.
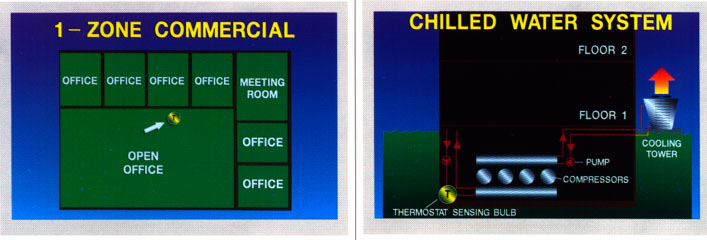
It is also a place for the thermostat is used as the primary control for one-zoned commercial system.

"All-to-Air commercial systems with a large number of temperature control zones, thermostat, which acts as the main element is located in the center of the air handling units in the departure of the air side of the cooling coil. Secondary thermostats are temperature control in each zone. For chillers, sensing thermostat bulb is in the water that enters or leaves from the refrigerator. All thermostats to recognize and react to temperature, but different types of this in various ways. Some thermostats are activated warping of the bimetallic strip.
In bimetallic element consists of two different metals are related to each other. Brass and Invar two metals used for this purpose. Bimetal device operates on the principle that different metals expand or contract at different rates during heating or cooling.
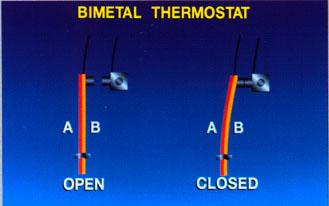
This electric cooling thermostat, temperature increase leads metal "A"to expand more rapidly than metal "B". This leads to the warping bimetallic strip. If the temperature rise is enough contacts, as shown to the right, alarm compressor. If it is used for heating, and not cooling, bimetal thermostat is designed so that the contacts to do with the temperature drop, and not with increasing temperature. This type of thermostat affordable, reliable and easy to maintain and adjusted.
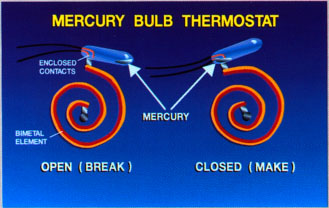
Total variation bimetal thermostat is mercury lamps thermostat. Its contacts are enclosed in a sealed glass ball, and not open to the atmosphere. Glass bulb contains a small amount of mercury that is rapidly sinking at the end of the smallest when the ball is tilted movement of a bimetallic strip. In this example, the metal outside bimetallic spiral expanding faster than what's on the inside. Therefore, the coils more tightly with increasing temperature and mercury closes the loop between two contacts, as shown to the right. This sends a signal to the commissioning of the compressor. Lowering the temperature causes the bimetallic element spins. When mercury moves to the other end of the glass bulb, it breaks the circuit and shuts down the compressor off. Because circuits control "makes" with growth of temperature, and "breaks" with changes in temperature, for example, shows the cooling thermostat.
Mercury bulb thermostat is a bit more expensive than simple bimetallic type, but it provides increased reliability, since the contacts are protected from dust and other contamination. It also provides a snap-action switches, which will be discussed later in this module. This electric thermostat is activated by a pressure than when driving bimetallic element. With both liquid and gas sensing lamp, pressure bellows increases as the temperature of the bulb increases. Bellows expands, mechanical closing the contacts cooling thermostat, or, as shown here, opening them for heating thermostat. Lowering the temperature of the sensing bulb causes a drop in pressure bellows and bellows contracts. Action opposite the temperature increase...
|





