Sectoral Use Of A Heat Pump
As mentioned earlier, the heat pump is a device that receives heat at a certain temperature and releases the heat at higher temperature. When managed to provide heat (e.g. for heating or hot water, heat pump is said to operate in heating mode; when operated to remove the heat (e.g. for air conditioning), it is said to operate in cooling mode. In both cases, more energy must be provided to drive the pump. In General, this operation becomes energetically favorable, if the total energy output greater than the energy consumed, the drive heat pumps and economically attractive if the total life-cycle costs (including installation, maintenance, and operating costs), lower than competing devices. The General heat source for the heat pump air, although water is also used in many applications. During the last decade the ground, or geothermal resources, more attention is to be used as a source of heat, especially in residential areas. From the sectoral point of view, the air is the most common medium of propagation, when the heat pump provides heating and cooling.
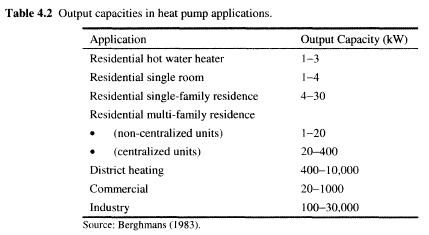
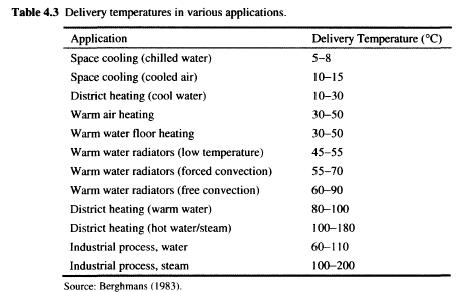
For the heating, air is also General secondary, except for those regions where many water distribution systems installed in the residential sector. The energy required to drive a heat pump normally provided by electricity and fossil fuels, such as oil or gas. General characteristics of some typical commercially available heat pump systems are listed in the Table. 4.1, in the residential, commercial and industrial sectors. For the commercial sector, all the basic characteristics similar to those in the residential sector, excluding fuel drive. In the former sector, a greater variety of types of fuel can be used because of the larger scale operation, which is suitable fossil engine systems. The industry also uses large result in greater fuel flexibility and heat source, as a rule, the waste hot water, steam or humid air. Radiator type will depend on the specific production process. The heating and cooling of single and multi-family houses has become the most successful application of heat pumps so far. A great variety of systems exist depending on whether they are intended for heating and cooling only or heating, the nature of the source of low temperature and the mean distribution of heat (cold) in building, air, water, etc). Heating-only heat pumps used in the residential sector in many countries where there is no air conditioning load. Units can be installed separately or as an optional accessory. While the performance, as a rule, higher than in existing systems, the main difficulty is that the higher first cost of the units can be restored only during the heating season, in contrast to the heating and cooling units, which are open all year. As mentioned previously, electric add-on heat pump is a system that can be used in combination with fossil fuel, furnace or Central electric warm air furnaces. For residential sector, output requirements of the heat pump vary depending on use, where such products are used, as indicated in Table 4.2. Requirements of the single family residence will range from 4 to 30 kW depending on the size, type and degree of insulation of the building. Multi-family building needs in the range from 20 kW to two family residence, 400 kW for residential block, although non-Central facilities attract smaller units. Depending on the size of the lattice, Central heating schemes can vary from 400 kW for localized applications up to 10 MW, for large-scale systems. The output needs of the commercial sector in a range from 20 kW to shops and small offices up to 1 MW for large commercial centers. The wider the range from 100 kW to 30 MW, is located in the industrial sector. Delivery temperature also varies depending on the particular application requirements. Table 4.3 describes the temperature requirements for a number of applications.
Heat pumps for residential heating and cooling can be divided into four main categories, depending on their operational function: Heating-only heat pumps for heating and/or water heating applications.
Heating and cooling, heat pumps for heating and cooling.
Integrated heat pump systems for heating, cooling, water heating, and sometimes heat recovery of exhaust air.
Heat pump water Heaters for water heating. Houses, heat pumps can be reversible air heat pumps (ductless packaged or split-type units). The heat pump can also be integrated in the exhaust air duct system or hydronic heat distribution systems floor heating or heat sinks (Central system). They often use air from the nearest environment as a source of heat, but can also be exhaust air heat pumps, or row on the air-to-air " and " water-to-air heat pumps. Heat pumps can be as monovalent and divalent where monovalent heat pumps meet the annual heating and cooling demand alone, while bivalent heat pumps are designed for 20-60% of the maximum heat load and fit around 50РІР‚95% of the annual heating demand. Peak load met with auxiliary heating system, often a gas or oil boiler. In large buildings heat pump can be used in tandem with a cogeneration system. In the commercial/institutional buildings heat pump system can be a Central installation is connected to the duct or hydraulic system, or multi-zone systems, where several of the heat pump are located in different parts of the building to provide individual space, air conditioning. Efficient in large buildings-water-cycle heat pump system, which includes a closed water cycle with multiple heat pumps are associated with a loop for heating and cooling with cooling towers and an additional heat source as a backup. In residential, commercial and administrative buildings, recently there has been growing interest in the room type of controlled heat pumps (Fig. 4.1). Besides some advantages such as greater comfort, noise reduction, and decrease energy consumption, some features of such a system are: Prevent exploitation when connecting to the wrong supply voltage or if the wiring is incorrect,
To prevent overheating of the compressor, the fan, the motor and the power transistor,
Detection of refrigerant low prices and evaporator freeze-up, and
Maintain a balance of pressure by management on/off cycle the compressor. 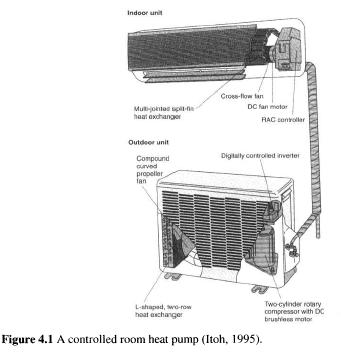
..
|
