Room Water-Cooled Condensers
Water removes heat from the metal surfaces approximately 15 times faster than air. Thus, water-cooled condensers much less than with air-cooled condensers. As usually, the water is cooler than the air condenser pressure and temperature can be below. As a rule, increases in water temperatures are allowed as it passes through the condenser. If the supply water temperature high temperature of the condenser will be high. Use caution to avoid freezing of the water circuit water-cooled radiates.
If the device is water-cooled, add 10F to 15F (6C 8C) water outlet temperature of the condenser. It wiH determine which refrigerant temperature should be. Correct head pressure can be taken from the refrigerant chart. The unit must be started so that these conditions are fair. If the head of the pressure exceeds this value by more than 5 kg, stop the compressor. Purge the system through the discharge valve sensor open for 10 seconds, 15 seconds. Then run the condensing unit again.
The trouble may be due to excess refrigerant or air in the system.
To determine this, stop the unit and cleaned before 15 seconds, 20 seconds. If the pressure drops a few, the trouble was air in the system. If the pressure drops, continue to delete a block. Clean up at the end of the condenser and liquid receiver full liquid refrigerant is cooled. Do not allow the temperature below 32F (0C), water pipes can freeze and burst.
Some condensing units have small valves, which can be used to check the fluid level. The level of the liquid sight glass is installed in several large blocks. It is connected to the top and bottom of the receiver. When pressure, liquid level in the sight glass will be equal to that in the receiver. This allows to quickly reveal the level of the refrigerant in the condenser and liquid receiver. You can easily judge whether this is the correct amount.
Always test the water leakage from the condenser outlet. There may be a leak between the water pipe and the refrigerant in the system. Unstable cooling and continuous oil, drinking or injection into the compressor points to an excess of oil in the system. This often happens at run time.
Common water-cooled condenser, the problem of formation of deposits of water on pipeline walls. Minerals normally found in solution in water are drawn to the walls of the condenser tubes. These materials include carbonate, sulfate, lime, iron and others, This electric process occurs because opposite charges, minerals and tubing. These deposits then act as a heat insulation layer. Cm. Fig. 15-57. If this layer can be removed, the capacitor must be replaced.
Two different operations necessary to clean the condenser:
- Prevention of scale,
- System cleanup.
Sulfuric acid-chromate solution is to prevent scale formation in open systems, such as evaporative cooling tower and capacitors. However, chromates are poisonous, and the absence of significant amounts shall be settled in the waterways. Always wear protective glasses, rubber gioves, and rubber bib aprons!
Sulphuric acid is a weak solution reacts with metal, of a Sulfuric acid in a strong solution reacts with copper. Better not use it to prevent formation of scale. Rough mixture of sulfuric acid and water can spoil the copper system of pipelines and steel structures. Some of the techniques used acid to start it, but it must be done quickly. Then it must be cleaned as soon as possible. Wear goggles and rubber gloves!
For cleaning of condensers, use only prepared chem. reagents. Carefully balanced cleaners, for example, of inhibited hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid, work well. They will not damage the equipment, if used properly.
Rusted capacitor can be recognized by checking the liquid line temperature of the refrigerant. Rusted capacitor will produce a hot liquid line, water-cooled condenser. (This is true, provided the amount of refrigerant is right and the other troubles have just mentioned are not found.) Temperature and pressure in the condenser will be much higher than expected. Eliminate all other possible causes of excessive water pressure. When these possibilities have been eliminated, severely corroded or dirty capacitor, probably the reason.
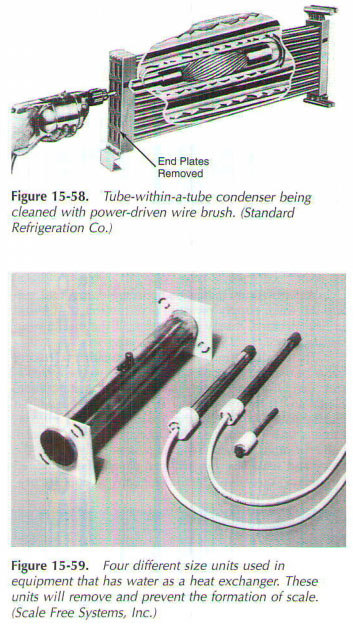
Soft sediment can be removed from some of the water-cooled condensers with a mechanical drive with a wire brush. This can usually be done without removing the capacitor from the system. However, the water circuit must be closed and the unit shut down. Always use new gaskets Assembly and tighten the screws and evenly.
There is a "scale-free" systems that effectively eliminate electrical processes, which leads fields. He exposes the electrolyte system water is treated. This is done through the use of a positive ground rod. This process, in turn, raises the electrical energy from the water, ft earthed outside of the boiler and condenser. Thus, inside the tubes remain free from scale. This electricity is also calls on the existing level or deposits to go back into solution. Then they are made through the system and discard.
 .. ..
|

 ..
..