Water-Cooled Condensers
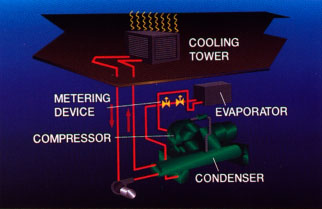
Water-cooled systems use a three-step process to reject the heat absorbed by the refrigerating system of the outdoor air. First, heat is transferred from the refrigerant in the condenser water flowing through it. Next, he moved from the room to the street using a water pump and pipeline, which leads him to the tower. Finally, the tower rejects the heat in the water, outdoors.
While this type condensing system more complicated, expensive and requires more routine maintenance than air-cooled systems, it is also more energy efficient. This allows the temperature of the refrigerant in the condenser to run about 15F lower than air-cooled systems. This means that the compressor operates on the head below the pressure and therefore consumes less electricity. Water-cooled systems tend to increase the popularity of the size of the system increases. In North America, they are the most popular in systems with more than 100 tons of cooling capacity. In some parts of the world, wider use of water-cooled systems.
Standard power range for cooling towers is about 5 to 3000 tons.
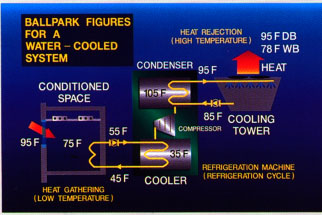
In a comfort air conditioning system under normal design conditions, the temperature of the refrigerant in the condenser about 105F. water inlet condenser starts about 20F below (85F) and increased by about 10F temperature, as it absorbs heat from the refrigerant. Water leaves the condenser about 95F, only about 10F below saturated refrigerant temperature.
Cooling tower spray 95F output water water cooled condenser for many parallel plates, exposing as much fresh air as possible. Fan air moves over these plates to increase evaporation. The lower the relative humidity of the air entering the tower, the greater the ability air absorbs the moisture that the process of the latent heat of vaporization takes the heat out of the running water. Each pound of water evaporated removes about 1000 Btu of heat from the water left behind. 10F a drop of water in the condenser from the time he enters the tower until he leaves the normal, with 85F water is sent back to the condenser to absorb more heat. The loss of water from the cooling tower through evaporation occurs when the water inlet connection attached to a float valve that keeps on a constant level in the drain pipe...
|


