Capacitor
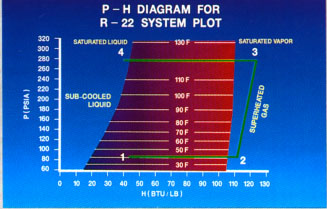
High temperature, high pressure superheated gas, leaving the compressor discharge at point 3, a condenser in basically the same condition. Saturation temperature 120F. This corresponds to a gauge pressure of about 263 PSIG which is the same as 277.7 PSIA, as is shown in our illustration.
As a capacitor that removes heat from the refrigerant, it enthalpy decreases. Move left from point 3 on our P-H chart, refrigerant, first loses overheating become saturated vapors. As it continues to lose heat, his condition is moved to the left of saturated steam for the queue to become a mixture of saturated vapors and saturated liquid. Couples, refrigerant, is a change of state, i.e., a condensation of vapor in the liquid. When saturated liquid line is reached, all vapor became saturated liquid. And even more heat is rejected, the refrigerant is becoming subcooled. He leaves the condenser (point 4) as the high temperature (105F), high pressure, supercooled liquid.
The total change in enthalpy of the refrigerant caused by the condenser is about 83 Btu/lb.
It is included in the 125 Btu/lb and leaves about 42 Btu/lb (125 - 42 = 83). Capacitor rejects from the refrigerant heat absorbed by the evaporator ("Refrigerant Effect") plus the heat added compressor (the"Heat of Compression"). It must cope with the compressor heat, while the evaporator is not necessary. As a result, capacitors, usually exchange about 20-30% more heat than evaporators.
..
|

