GLAZE LOW TEMPERATURE COIL
When the surface of the evaporator coils operate at temperatures below 0C (32F)and below the dew point temperature of the air, frost will be formed on the coil. In special situations, icing situation can occur where the moisture from the air the first condenses to a liquid water, then freezes ice. A much more common situation is when the water vapor turns directly in solid state frost. No redeeming merit was discovered frost, not General ways of preventing formation known.
Agreeing that we must live with frost, for cooling air in cold temperatures approach is to lessen his execution, and remove it periodically. Two negative consequences frost brought mosf often are: (1) the resistance to heat transfer; and (2) the restriction of air flow.
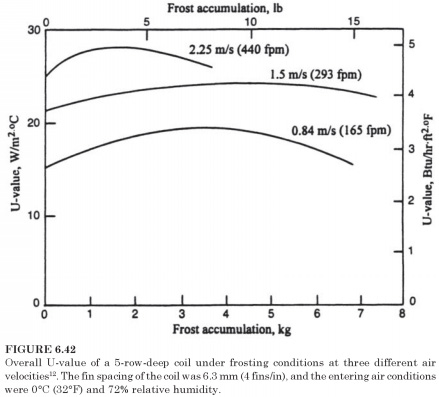
These two penalties, limiting the speed of the air flow is the most serious. Some laboratories tests12 were held where the air velocity is maintained constant gradual increase in the power of the fan while the frost accumulated (Fig.
6.42). These tests showed that the value of U has not been reduced, as long as the flow rate and speed remained constant. Drop in air pressure, on the other hand, increases markedly with additional frost, as shown in Fig. 6.43 shows".
Fan-coil units operating in the region are unable to maintain a constant air flow rates, as frost accumulates, in contrast to the way the tests in Fig. 6.42 and 6.43 conducted. Instead, due to its pressure and flow characteristics, the fan will deliver a lower air flow and pressure drop increases. This decrease of the air flow and reduction in the speed of air flow, reduces the U-value, as shown in Fig. 6.42 the show, and is the main reason for the decrease of the heat transfer rate. This, combined behavior of the fan and coil proposes criteria for perceive the need to defrost: air-pressure drop across the coil or the air flow.
When choosing coils work under icing conditions, the designer must be connected to coils with wide spacing and a large heat transfer area. Fig. 6.44 shows some experimental data13 demonstrating that the coil with a wide finspacing not subject to the rapid rise in air-pressure drop experienced coils with closely spaced fins. Another goal is to choose large coil with a low temperature difference between air and refrigerant. In favour of this choice (see Section 6.17) is the low speed of removal of moisture and, consequently, less rapid frost.
 .. ..
|


 ..
..