CAPACITY CONTROL
Almost all refrigeration units are subject to various cooling load and, in General, the plants are operating at part load. Capacity must be reduced, otherwise boiling temperature would drop until the performance of the plant corresponds to the load. The boiling temperature is too low, it may damage the product. Small plants and just cycle the compressor on and off, to ensure time-average match potential for download. In large plants the opportunity to modulate the capacity of at least 25% of full capacity is desirable. As the cost of variable frequency drives reduces and increases their reliability, this method of modulation performance may become more prominent. Currently, however, cylinder unloading-standard method for regulation of the pumping capacity of reciprocating compressors.
Multicylinder compressors can be downloaded, open the inlet valve on the cylinder. During the reception and stroke draws suction in the compressor, but then on its reverse, instead of vapor compression piston pushes the refrigerant back to the suction.
Suction valve may be of the open valve-lifting contacts, which, in turn, is produced by oil lubricating oil pump or gas injection, which is controlled by an electromagnetic valve. In some designs, the normal location of unloaders is that the oil pressure is required to enable compression. This mechanism will automatically start the compressor cylinders unloaded because the oil pressure is not available until the compressor at least partially up to speed. Two variables that are most often felt to regulate the operation of the cylinder unloaders are suction pressure or output temperature of chilled liquid in the evaporator.
To specify performance at partial load, compressor manufacturers usually involve the required power relations during the unloading of the cylinder, as shown in Fig. 4-20. This schedule can be applied to the 8-cylinder compressor that can unload 2, 4, 6 cylinders. To work at 60% of capacity, for example, the compressor will be switched between half-unloading and one-fourth-unloading conditions. Percentage of full capacity corresponds per cent of the total pumping cylinders, but the power requirement is several percent higher than a linear relationship.
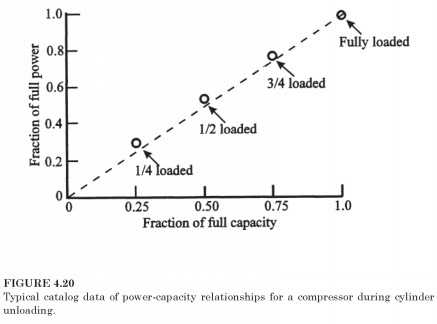
Friction values in pumping idle piston is to be expected, but there is compensation a positive impact. In part-load operation, the condenser and evaporator heat transfer rates fall, so condensing temperature falls and the boiling point increases. Both effects reduce power and compensate losses from idle cylinders...
|

