Cooling towers
In some areas water contains chemicals that makes it unsuitable as a coolant. In other localities, the water can be very few, expensive, or its use may be restricted by law.
Cooling towers to save on water consumption, These towers serve the same purpose as the spray towers used in large industrial refrigeration systems. A variety of tower designs, are shown in Fig. 13-44. The tower produce excessive noise due to their large fans and splashing water. They should be located away from areas such as offices, restaurants and residential quarters.
The following factors affect the cooling performance:
- Design conditions.
- Humidity requirements.
- Tower heat load.
- Design wet bulb temperature.
- The quality of water.
One system connects the condenser water line coil water in the body. The pump forces water through condenser and then through the coil in the tower. Tower coil pierced with holes, and the water is sprayed into the housing. The air rushing through the spray of the water evaporates.
Evaporation cools the remaining water from the outside air temperature or even below (wet bulb temperature). In some systems, motor-driven fans control the flow of air through the tower. Fig. 13-45 shows the cooling tower fan consh'ucted primarily from fiberglass.
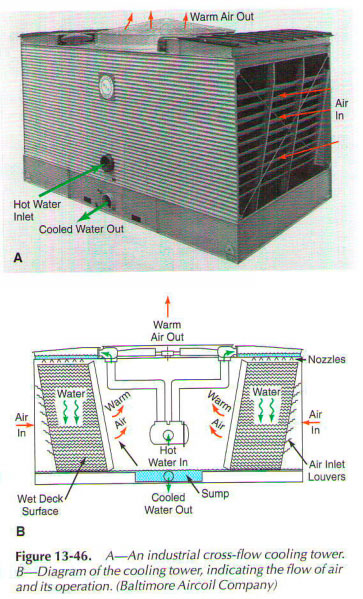
The flow of the cooling tower, which takes water from the source of heat through the inlet on the side of the device to the hot water distribution basins on each side is shown in Fig. 13-46. Gravity flow distribution nozzles water evenly over the wet deck surface. Air is drawn in through the air intake louvers and wet deck surface, causing a small part of the water evaporates, removing heat from the remaining water. Cooled water then flows into the lower pallet and returns to the source of heat.
The cooled water is collected at the bottom of the chassis. It passes through the Masach, which removes leaves or other foreign matter. He then recirculated air through the condenser. Float-operated valve in the bottom water pan add more water as needed. This float works as a refrigerant of low side of the float mechanism.
Stoke constantly bleeding a little water from water pan. This saves the hardness of water to a minimum. Chemicals can be added to retard rust, algae, fungi growth, and the like. Cooling towers, made of corrosion resistant materials. Among them steel (zinc-dipped after Assembly), copper, stainless steel, plastic, or treated wood.
The more surface water in contact with the air flowing through the tower, more efficient cooling action. Most of the towers were some agreement that the water flows over materials in thin films. This material is usually called the fill. Fills made many of the materials: metal fins, wooden slats, plastics, asbestos-plastic, and asbestos. Forms of the surface ranges from Z-shaped, SOT, embossing, flat sheet of corrugated sheet. Cellular (mobile) fill is becoming very popular. Distribution system (nozzles, gutters, V-grooves) should be kept clean and must distribute water evenly to prevent accumulation of precipitation.
Usually, cooling towers no danger of freezing during work. However, electric heat will keep the water to a temperature during stops. Dive and convection heaters have been used for this purpose. Electric heater can be installed in the pump circuit. Hot water or steam can be used to prevent freeze-up reservoir. Pipes may need to isolate or electric heater tape.
Overflow pipe, cooling towers, carry excess water drainage system. Some have airflow control, to prevent freezing if wet or dry bulb temperature falls below 32F (0C). Exhaust thermostat fan in shock. Use only the screens pump-injector. sure that all of the suction line below the water level in the tower. Otherwise, the air may enter the suction line. As a result of the fall of the pump volume may damage the pump.
Pump outlets, on the other hand, need in thin screens. Water pump for pumping water through the system. This will avoid the low water pressure in the condenser pipes or tubes. The tower evaporates about two gallons of water each hour for every ton of cooling power. A liter of water weighs about 8.3 kg (3.76 kg). About 970 Btu (2,257 kJ) are required to evaporate into one pound of water. The number of units to evaporate into one gallon of water is determined by multiplying the weight (8.3 pounds. or 3.76 kg) by the number of Btu/lb. or kJ/kg (970 Btu/lb. or 2,257 kJ/kg). Thus, evaporates gallon of water, 8,051 BTU or 8,486 kJ required. Evaporate two gallons will require 16,102 BTU or 16,972 kJ. For details of the tower sizes and capacities, see manufacturers ' catalogs.
 .. ..
|

 ..
..