Milk and dairy products
Milk is converted to the Creamery and associated plants, fully or 'market' milk, skimmed milk, cream, butter, cheese, dry milk whey, yoghurt, butter, condensed milk, milk powder and ice cream.
In the dairy industry in General, the basic needs for mechanical cooling:
- Cooling of milk directly after the release of the cow, and before transportation to the Central Creamery
- Storage of raw milk to cool down after its entry on the Creamery
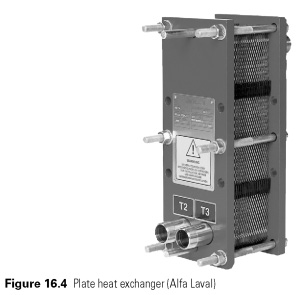
- Chilled water for the use of plate heat exchangers for cooling milk and dairy products directly after pasteurization
- Chilled water to wash oil
- Chill temperature shops for milk, butter, cheese, yoghurt and other liquid dairy products
- Frozen storage for butter (and sometimes cheese)
- Continuous, plates and air blast freezers for ice cream
- Low temperature brine for freezing ices
Milk from the cow, about 37C and you want to cool for 2 hours to 4C or below, under hygienic conditions. At this temperature, in any microorganisms present will multiply at a dangerous speed and milk may be transported on a cheese factory.
Dairy farms mass storage milk tanks with their own refrigerators.
This is usually in the form of double skin insulated tank, having the evaporator in the jacket. Stainless steel clicking the formation of the jacket is an allocation system for evaporation of the coolant, which comes from the condensing unit. Load is intermittent, relevant milking times and the temperature of the milk must be rapidly reduced. To reduce the size of the equipment for cooling ice banks are sometimes used for pre-cooling of milk before he enters the tank. In the cooling system, runs for 24 hours and forms a layer of ice on the surface of the evaporator coils, when there is no milk cooling load. This stored cooling effect will help cool the warm milk, when required.
Bulk tanker vehicles will not collect milk, which is warmer than 4C. If the milk can be collected from the farm in this temperature bulk tankers, vessels and transported quickly enough to the Creamery, no need for refrigeration equipment in the car. Upon arrival at the Creamery milk tested and transferred to bulk storage tanks, which can accommodate up to 150 tons each. These will be largely isolated and may have some way of cooling, so as to keep the milk to 4C until it passes into the processing line.
During the follow-up processes, milk and dairy products requires cooled to 4C or so. The primary method of achieving this is by using chilled water at a level just above the freezing point, as a secondary refrigerant. Oil have a great Central water cooling system using Baudelot or spray coolers or chillers. Chilled water is supplied all cooling within the company.
Whole milk for human consumption is pasteurized at 75C for a short time, and then cooled to 4C immediately. This is done by contraflow heat exchange between milk at the input and output of the process, hot water and cold water plate heat exchangers (see Fig. 16.4) in the following stages:
- Raw milk at 4C is heated by the outgoing milk to 71C.
- This milk, finally, heated hot water to a temperature of pasteurization 75C-or above UHT milk) and held for a few seconds.
- Milk is cooled incoming milk, about 10C.
- The final stage of cooling from 10C 4C using chilled water 2C.
Milk and other products are processed:
- In a centrifuge to produce the cream and skim milk.
- In churning devices make butter and buttermilk.
- With to make cheese rennet (leaving serum).
- With sour bacteria to make yogurt.
- As a result of drying, dry milk.
Butter is made from cream continuous churning machines. The stages of this process, butter, then washed in clean, cold water to keep it cold and remove excess kefir. At the end of whipping stage, butter still in the plastic state, and after packaging must be stored in 5C compile fat. Long-term storage of oil in 25C.
Cheese can be pressed into a homogeneous unit, or to the left to settle depending on type and methods of production. Then they go through the period of maturation, to give the characteristic flavour and texture. In the cold cheese ripening period should be under the strict conditions of high humidity and hygiene, or cheese will be damaged. Some cheeses can be frozen for long-term storage, but then should be allowed to gradually thaw and complete their maturation to their release on the market.
Other processes (except for drying of milk) require the finished product to be cooled to the desired temperature storage is usually 4C or so, and store in a cool place up to the point of sale. The usual type of refrigerating chambers can be used for mixed dairy products, because they would all be Packed and sealed after manufacturing.
 .. ..
|

 ..
..