Secondary coolants
Where a secondary refrigerant is circulated and working temperatures below 0C, some forms of non-stop mix should be used. Aqueous solutions of sodium chloride and calcium chloride were the first type of sub-zero secondary fluid, and therefore the collective term is sometimes used brine. Propylene glycol-water mixtures of the most widespread glycols used as secondary refrigerants in the refrigeration and allowed where contact with food is possible. Ethylene glycol is a different type and there are many other products on the market, some of which do not contain water. Thermophysical properties of Propylene glycol-water mixtures are shown in Fig. 12.1 .
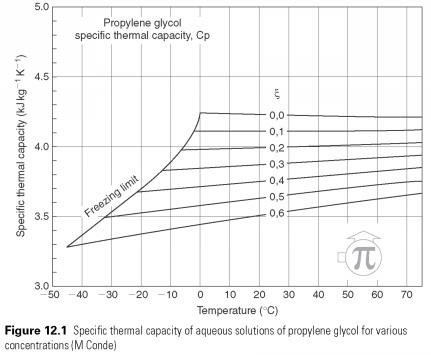
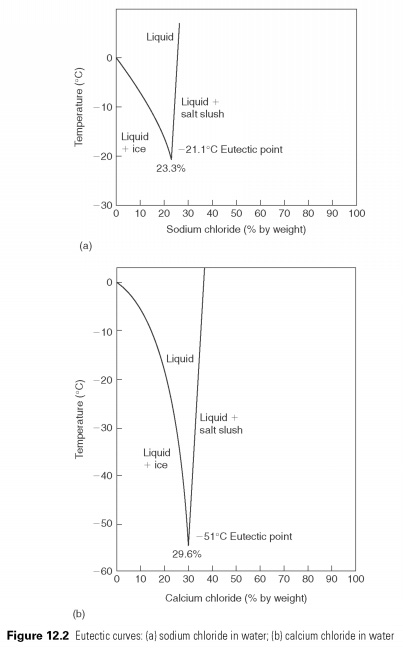
Any decision will be one of concentration that remains liquid, until it reaches the freezing point, and then it will freeze. This eutectic mixture, and its freezing point-eutectic point of dissolved substances (see Fig. 12.2). On all other concentrations, as the solution is cooled, it will reach the temperature at which the excess of water or solution, will crystallize out to form a slushy suspension rigid body in a fluid, until the eutectic point is reached when all freeze.
For the economy of costs and reduce viscosity (and so improve heat transfer), decision weaker than eutectic are used, as a rule, in the absence of a risk of freezing in the evaporator.
The concentration of the dissolved substance renders significant influence on the viscosity of the fluid, and on the surface convective resistance to heat flow. There is little data published on these effects, so that applications should be checked from basic principles.
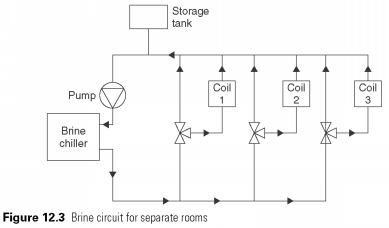
Brine can be injected for each of the cooling device, and control the flow through disable or bypass valves to maintain the required temperature (see Fig. 12.3). Brine pump, as a rule, in the return pipe for cooling, as shown in the figure, so the pumping rate is based on the return temperature, density.
Where the brine system services license temperature for example, a number of food shops, coolant can be too cold for some conditions, causing dehydration product. In such cases, to cool these rooms brine to be mixed. Private three-way mixing valve and the pump will be required for each room (see Fig. 12.4).
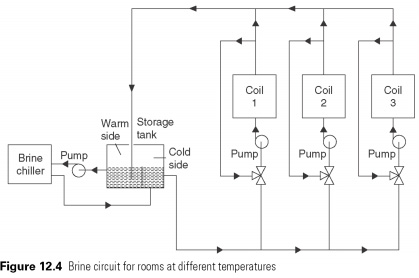
with the divided tank, as shown in Fig. 12.4. except that the tank will be, with separate feed and expansion tank. To reduce the effects of corrosion inhibitors are added, as a rule, chlorate sodium salts of sodium and phosphates in glycols. These alkaline salts and counteract the effects of oxidation, but periodic inspections shall be taken, and the Boers or similar alkali is added if the pH falls below 7.0 or 7.5.
Brines hygroscopic and will weaken the absorbing atmospheric moisture. Checks should be made on the strength of the solution and more salt or glycol is added as necessary to maintain the freezing temperature to the desired value.
|




